目宿世界上支流的原子钟(光晶格钟)的区别次要有哪些?
先挖个坑,根据地域大要列一下有哪些机构在做那件事儿,然后再根据中性原子的品种大要介绍一下各自的特点以及一些前沿的工具
亚洲:
KRISS(韩国尺度研究院,Ytterbium)
Tokyo University(日本,Strontium/Ytterbium/Mercury)
NMIJ(日本,Yb/Sr)
NICT(日本,Sr,fiber link with University of Tokyo)
NIM(中国国度计量院,Sr)
NTSC(中国国度授时中心,Sr)
WIPM(武汉物数所,Yb/Hg)
SICM(上海光机所,Hg)
ECNU(华东师大,Yb)
大洋洲
UWA(Yb)
美洲
NIST(Yb,Andrew D. Ludlow)
JILA(Sr,Jun Ye)
UA(Hg)
(目前来说NIST和JILA的钟的目标更好)
欧洲
PTB(Sr)
MPI
INRIM
SYRTE
to be continued...
2021.06.26
我觉得我极有可能鄙人周把2年前挖的坑大要填上!!
2021.07.04 03:30 开更
(打了半个小时编纂一个表格里的公式间接谜底不见了,并且知乎在小我主页上还找不着草稿保留,我整小我都麻了)
(在问题详情页编纂再次瓦解,再也不敢往表格里面插公式了,我就间接latex格局了)
(因为涉及内容较多,若是有刚好做到此中工做的同窗或前辈看到有错误或者需要弥补的欢送提出,会在时间允许根底上讨论并做出修改)
那个问题是在2018年进组“打工”时提出的,其时看到世界上那么多做“钟”的,出格是看到一个尝试室为了做成一台光钟所消耗的人力、物力、财力那么庞大,就想为什么世界上那么多组不同一找一个原子做一个型号的钟呢?
如今颠末3年的时间,固然在那个研究标的目的还没有做出任何新的奉献,但希望雁过留痕,又刚好给老板做了一版光钟的PPT(较多内容参考小组内师兄师姐以往的PPT,缝合怪再添加看的一些比来尝试停顿,包罗紧凑型光频标,核光钟等),能为后来的人供给一点快速入门的领会就没白搭那三年的干熬。
起首我想把原标题问题中的原子钟的概念拓宽到频次尺度上,或者也能够说成时间尺度,因为实正的原子钟间接输出的能够为THz(光频),GHz(微波射频)的奇奇异怪的数字,但在尝试中总有办法把那些奇奇异怪数字的频次尺度转化为可间接用于射频设备(好比斗极,好比DDS所需的100 MHz,10MHz,1pps等,那个涉及到PLL,光学频次梳等内容,等有时机再填那个坑)
在时间标准上,世界范畴内的频次尺度根本能够分为以下几类:
TickerCounterEarths orbityr^{-1} ≈ 32 nHzCalendarPendulum clock1 HzEscapement, gearsQuartz watch2^{15} HzMicrochipMicrowave clock10^{9} HzElectronic oscillatorOptical atomic clock10^{15} HzFrequency comb从以上表格能够看到,最早的通过地球的公转做为时间尺度,一年的标准算下来频次为32 nHz,再到摆钟1 s一次,到石英钟2^{15} Hz,分辩率是在不竭进步的,再到用原子的能级来计时,微波钟以及光钟(以及将来可能的核光钟等)。此中的思绪是尽可能找到不受外界情况影响的频次参考,从公转,到钟摆,到石英振荡器,到原子内部的能级跃迁,同时频次的Ticker量级不竭进步,能将时间测得更精准。
时间测得更精准那个概念很广泛,但详尽来说一般有两种目标评价一台钟的精准水平,包罗禁绝确度(inaccuracy)和不不变度(instability)。
那两个概念在没有认真区分前很容易混淆,以打靶为例(下图),准确度一般指输出频次的准确性,而不变度则指频次的复现性,前者能够对应微波射频晶振的温漂等特点,然后者在低频段不常存眷。
(a)较好的禁绝确度和不不变度 (b)较差的禁绝确度和较好的不不变度 (c)较好的禁绝确度和较差的不不变度 (d)较差的禁绝确度和不不变度
在以下讨论中后者不不变度会经常涉及而且是光频标的一个重要目标,其能够表述为
此中坐标是随均匀感化时间/积分时间不竭变革频次的阿伦误差,右边是其有关因素的计算,除开常数外,包罗钟跃迁谱线的信噪比、品量因素Q(ratio of linewidth Δν to its frequency ν_{0} )和τ的指数p,关于被动型(p=1/2),关于主动型(p=1,在理论上也可能用纠缠体例实现),此中关于光钟中被动型是指有一束钟激光,钟激光时刻与原子的(一般为极窄线宽,但关于紧凑型光频标也纷歧定)响应能级实时共振,即钟激光参考在原子的跃迁能级上,此为被动型;主动型为激发原子,使得原子在特定情况下受激辐射出光频标响应能级的光子(为北大陈景标教师提出,好坏腔一体化双波长主动光钟,有一些初步的理论计算[1],但尝试上实现起来以目前的科技程度较为困难);
针对以上表达式,进步不不变度的体例:
通过冷却原子降低钟跃迁谱线的线宽Δν进步钟跃迁谱线的信噪比,例如通过增加原子的数量等找到频次更高、线宽更窄的原子跃迁(当然那会受限于目前所能到达的激光频次,有时候原子跃迁频次能到达x射线,以至nm以下,但目前没有能做出那个波长的激光器)下面起头进入正题,光学原子钟(optical atomic clock)按原子类别进一步联系关系到囚禁体例可大致分为两类:中性原子光晶格钟(Neutral optical lattice clock),离子光钟(ion optical clock)。留意到中性原子光钟区别于离子光钟在于离子光钟一般为Paul阱或其改良版囚禁单个离子,而中性原子则通过偶极阱囚禁较大都量的原子,那个区别会招致最末光钟的不不变度和不确定度评估上有着显著的差别,但最末那两类光钟间接输出的都是钟光频次信息,即为光钟。
一、中性原子光晶格钟(Neutral optical lattice clock)一般接纳碱土金属(如锶Sr,镱Yb,汞Hg等),其典型跃迁能级图[2]如下
Simplified energy level diagram representative of many group 2(-like) atoms. Some of the most relevant transitions are indicated with arrows, and their wavelengths(in nanometers) and natural linewidths are specified in the adjacent table for the case of Sr, Yb and Hg一般而言,因为中性原子光晶格钟囚禁了较大都量的原子,为钟跃迁谱供给了较好的信噪比,使得其在不不变度出格是秒稳上优于离子光钟。(但近期2020WIPM的钙离子光钟评估出来也能在长时间后到达和光晶格钟同样级此外E-18长稳)
中性原子光钟中次要用到的能级1S0-1P1(a),1S0-3P1(b),1S0-3P0(c),3P0-3S1(d)、3P2-3S1(e)、3P0-3D1(f)
此中(a)、(b)常用于冷却原子,例如塞曼减速、磁光阱,(c)则为窄线宽能级,一般常用于钟光输出的能级,d、e、f则为抽运光
关于抽运光,有一个很重要的原因是窄线宽对应的概能级寿命相较其他较长(秒级别),颠末钟激光激发的原子需颠末很长时间才气回到基态被探测,抽运光则是加速那个过程,相反,若是没有抽运光无法构成闭合的能级轮回,典型的处理办法有量子逻辑光谱(通过探测另一种与其有库伦彼此感化的原子的形态来判断钟激光能否激发了原子,并且另一种原子凡是和其在库伦彼此感化下通过协同冷却配合构成冷原子团);而d抽运光则是因为3S1态的原子固然有部门几率回到1S0态被探测,但仍有相当多的原子自觉辐射到3P2态,需要通过(e)过程不竭搜集3P2态的原子到1S0态以停止探测;
对应于以上能级,整个钟探询周期以及造成胜利的钟整体的过程为:原子的冷却与囚禁->冷原子在光晶格中的拆载->钟激光激发->探测被钟激光激发原子的比例(电子弃捐法,aka归一化探测)->闭环
在获得冷原子的根底上,扫描钟激光频次能够获得囚禁在晶格中的载波边带谱如下[2]:
Spectroscopy of the clock transition in the optical lattice. When the clock transition is strongly driven into saturation, the motional sidebands can be easily observed. From these spectra trap parameters such as motional frequency, trap depth, Lamb-Dicke parameters, as well as t
载波边带谱能够反推出势阱深度、原子的温度等信息,进入载波后细扫则能够获得~Hz级此外谱线,那里能够大要算一下Q值(Q = 1E15 Hz / 1Hz = 1E15,是相当高的了!)
(a) High resolution spectroscopy of 87Sr yielding a FWHM linewidth of 0.5 Hz. (b) High resolution spectroscopy of 171Yb, yielding a FWHM linewidth of 1 Hz
以上就是中性光晶格钟的整体性原理,以下是其略微更细一点部门。
1.1 镱(Yb)光晶格钟次要研造单元有:NIST、KRISS、RIKEN、iNRiM、NMIJ、ECNU、WIPM
Simplified 171Ytterbium Energy Level
镱有诸多同位素,此中常用于做钟的为费米子171Yb,核自旋为1/2,有较小的碰碰频移而且因为核自旋为1/2在磁场团结下1S0和3P0均团结为2个磁子能级,能级简单;
171Yb光晶格钟响应应波长及其功用
2021.07.07 暂时鸽了 暑假再更
2021.07.30 开更
2021.08.01. 4:36 更几算几
光钟的复杂水平次要来源于需要多路激光,差别的激光有差别的感化,在过程上可简述为:冷却→囚禁→拆载→探测→闭环
简单来说获得温度较低的冷原子团(<10uK),拆载在光晶格中/离子阱中,在钟激光的感化下,晶格场/离子阱势场抵消反激动量,获得高精度(~Hz)钟跃迁谱线,随后将钟激光器锁定在较低温度的原子那个参考系统上,整个过程在颠末闭环锁定后即可认定为造做出了一台光钟。
以以上表格为例,399nm (6s2 1S0→6s6p 1P1)次要用于大规模捕捉高速运动的原子,一般将原子冷却囚禁在磁光阱中(Magneto-optical trap, MOT[3]),一般温度为(几百uK~mK),颠末二级冷却556nm(6s2 1S0→ 6s6p 3P1)获得~10uK级此外冷原子团。当然冷原子团的获得并非那几句写的那么简单,需要考虑的包罗激光的失谐量、偏振、和磁场梯度的婚配、光斑大小、光斑准曲水平、光斑量量、光强功率的对称性、光强的不变性、光强(3个标的目的上)平均性等,那些需要考虑的细节只要一个出问题,都无法获得冷原子团的荧光信号。
最末将那些冷原子团拆载在偶极阱(Optical Dipole Trap, ODT)中。偶极阱的波长涉及到魔术波长(Magic Wavelength)概念,最早由H. Katori提出[4],因为偶极阱中存在AC-Stark效应,会对钟跃迁578.4nm(6s2 1S0 → 6s6p 3P0)的基态与激发态的能级产生频移,魔术波长的偶极阱中上下能级的频移量相等,在σ+或σ-的钟激光跃迁时不引入而外的频移,响应的偶极阱波长称为魔术波长,需要留意的是,因为斯塔克频移和能级有关,因而选用差别的钟跃迁所需要的魔术波长纷歧定不异。 因而在做双钟频跃迁时需要两套差别波长的晶格光。别的还需要提的是抽运光(repumping laser),那点中性光晶格钟比力经常利用,因为响应波长有成熟的激光器,可以用来构成闭合的跃迁,以完成闭环所需要的归一化探测(也称电子弃捐法探测),与之相对应的为Al+光钟,没有闭合的跃迁只能通过量子逻辑光谱体例用协同冷却时利用的逻辑离子来帮忙判断钟光能否与粒子在时刻连结共振。
美国NIST获得的1.4Hz拉比谱[5]
在获得拆载在魔术波长光晶格中后,最重要的是获得窄线宽的钟跃迁谱,以NIST获得的拉比谱为例,钟激光通过AOM-0(AOM,Acoustic optical modulator,声光调造器,其操纵超声换能器将射频场转换到晶体上构成光栅,光栅的刻度与射频信号成比例,颠末光栅的激光发作衍射,衍射差别的级次有差别的移频效果)后别离经AOM-2送入两套实空腔,实空腔中为399nm、556nm、759nm造备的冷原子团,通过扫描AOM频次能够获得超窄线宽的钟跃迁谱线。
美国NIST 171Yb光晶格钟不不变度评估表
目前报导的更好的Yb钟在不不变度和不确定度上均已到达E-18级,此中不不变度为3.2E-19@10^5 s,不确定度如上表为1.4E-18[6]
下面放几张目前国内华东师范大学光谱尝试室的171Yb的比来停顿
ECNU LPS 部门171Yb光晶格钟光路
The schematic diagram of absolute frequency measurement of 171Yb optical lattice clock.
The instability of in-loop operation and synchronous frequency comparison which shows an instability of 1.28×〖10〗^(−15)∕√ , reaches 9.1×〖10〗^(−18)over 20000s[7]
The absolute frequency values of 171Yb clock transition measured by different laboratories, The blue solid line and the shaded region represent the CIPM recommended value and its uncertainty, respectively[8]
1.2 锶(Sr)光晶格钟次要研造单元有:JILA、RIKEN、NMIJ、PTB、LNE-SYRTE、NIM、NICT、AGH University of Science and Technology
与Yb差别的是,Sr同位素较少,次要用来做钟的同位素有费米子87Sr和玻色子88Sr,87Sr常用跃迁如下图:
Level diagram of relevant states and transitions in 87Sr
其常用波长及其功用如下
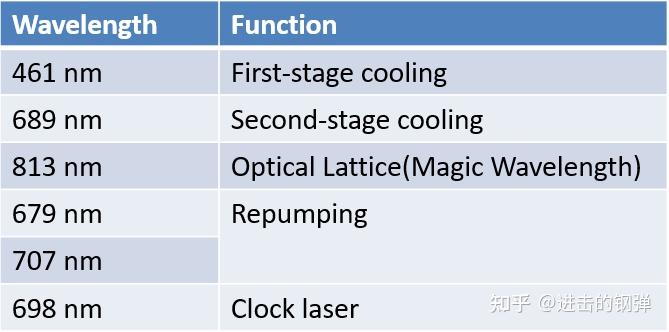
87Sr常用激光波长及功用
与前面Yb的能级大同小异,但有些许差别的是在一级冷却MOT中,1P1 87Sr原子由极大要率经1D2落到3P2,3P1,构成冷却的黑洞严峻影响一级冷却捕捉原子效率,因而在461nm的蓝MOT中参加抽运光679nm,707nm会进步捕捉效率,接下来介绍一些比来比力新的停顿。
2021/08/07 1:55继续更
1.2.1 JILA实现的费米简并的三维光晶格钟[9]
Schematic showing the propagation direction (large arrows) and polarization (double arrows) of the 3D lattice and clock laser beams.
实现了费米简并水平的光晶格,丈量温度为0.2~0.3费米温度,在给定量子化轴磁场B的标的目的上通过斜打一束钟光能够看到边带冷却的成果红边带以根本消逝
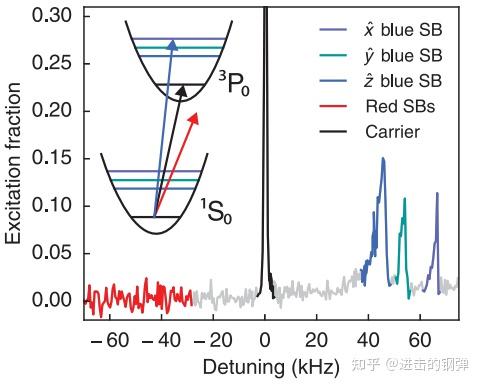
Motional sideband spectroscopy using the oblique clock laser shows no observable red sidebands, illustrating that atoms are predomonantly in the ground band of the lattice
并在两台三维光晶格钟的同步比对下获得了秒稳3.1E-17,长稳5E-19@3600s的好成果
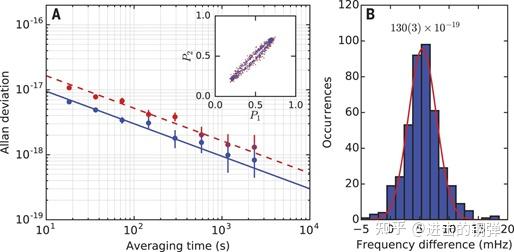
(A) The Allan deviation of the differential frequency shift between two independent regions of the 3D lattice.(B) A histogram of the measured frequency differences for an averaging time of 2.2 hours and 3000 atoms. The fitted Gaussian gives a fractional frequency difference of 12
1.2.2 日本H.Katori实现的可搬运/冷腔/腔加强型Sr光钟冷腔光钟[10],寡所周知,因为黑体辐射的存在温度高于绝对零度的物体在无时不刻通过热传导、热对流、热辐射等体例向外辐射电磁波,在常温(约300K)情况中,腔体、外界情况不竭向光晶格中的冷原子辐射热量,那会使得钟跃迁能级产生频移而且引入响应的不确定度,在早期的光钟评估中,一般黑体辐射(Blackbody radiation)在E-16量级(不做任何控温情况下),另一个主导项是光晶格(频次与功率的起伏引入的光频移),Katori提出冷腔的思绪,在原子实空腔中设想一个低温的冷腔,通过主动控温将腔体温度降低至约100K,在钟光探测前通过调谐光晶格另一束光频次将原子挪动至冷腔内,钟光在冷腔情况中对原子探测,随后再将原子移出冷腔停止抽运和荧光探测。通过那种法子将BBR有效降低至E-18量级,鞭策晶格光钟不确定度到新的高度
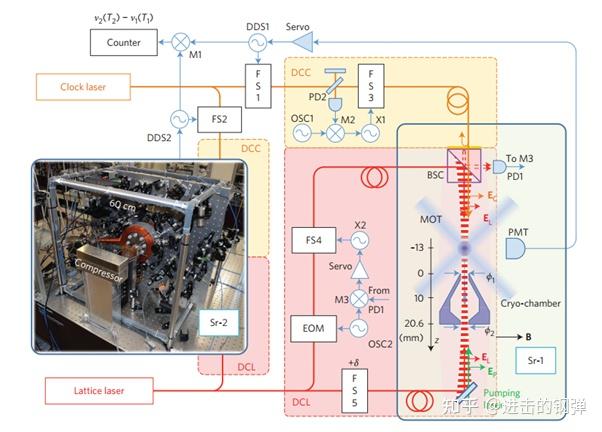
Experimental set-up of the cryogenic optical lattice clocks
尝试安装如上图,冷腔即为图中Cry-chamber,有了以上安装能够很便利丈量差别温度下黑体辐射频移对钟跃迁频次的曲不雅影响(比拟以前仅能通过有限元阐发大致定量计算或者通过热探头计算温度梯度,进而评估BBR影响)

Temperature-dependent BBR shift. a, clock excitation spectra measured at T- 95 K and 296 K. b, Frequency difference between two clocks
最末Katori组对冷腔光晶格钟评估得到不确定度为7.2E-18,有了如斯高精度的钟他们能够间接操纵光钟停止大地丈量。

在2020年[11],Katori组将研造的两台87Sr可搬运光钟搬运至约450m 高度差的东京播送电视塔上查验广义相对论。寡所周知,广义相对论中把引力场的起源为时空的曲率,预言了差别引力场的时间扩张纷歧,即引力红移。

广义相对论对频次和引力势场的语言
式中α代表了现实偏离广义相对论的系数,丈量该值对广义相对论的验证有重要的意义。[11]光钟查验广义相对论将丈量精度从E-2进步到了E-5量级,最末操纵两台光钟的丈量成果为在Δh≈450m, α=(1.4±9.1)E-5。
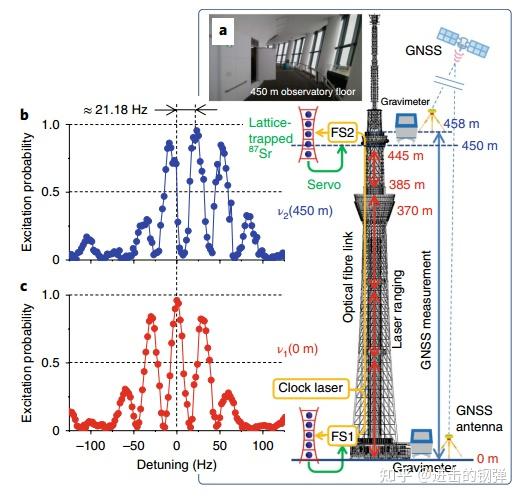
RIKEN&amp;#39;s two transportable optical lattice clocks testing the General Relativity(GR)
2021年,Katori组在[12]报导了他们所用的可搬运光钟的详细构造,让我们有时机一窥那强大的hold才能(做一台光钟就已经很复杂了,出格是冷腔、腔加强等手艺的实现,做一台工业化可拆配的高不确定度光钟则是代表了N多人的共同和心血)
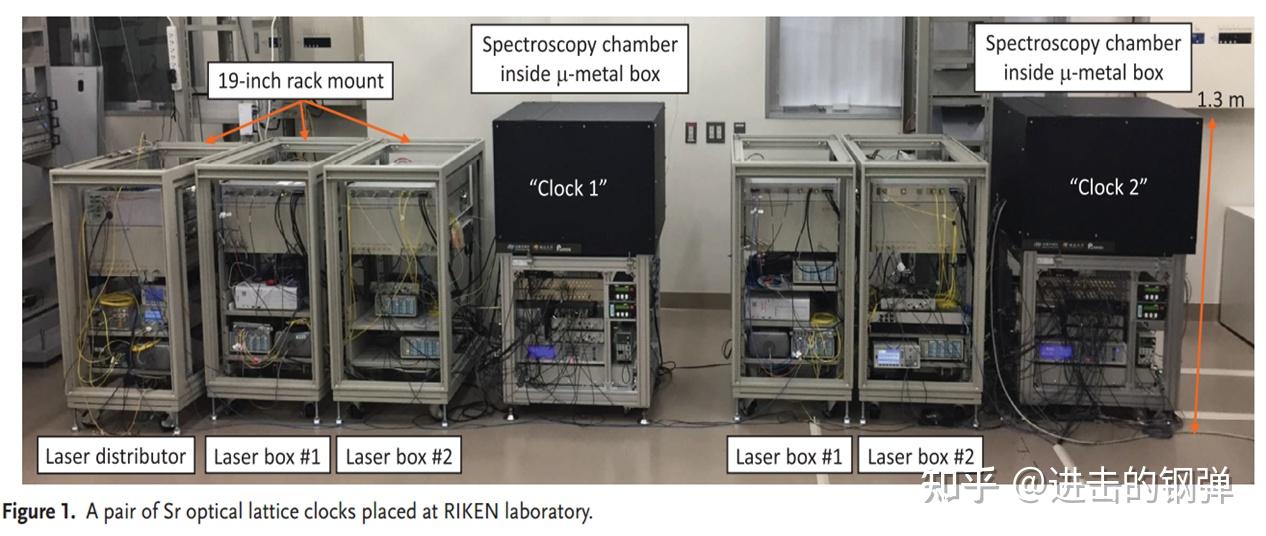
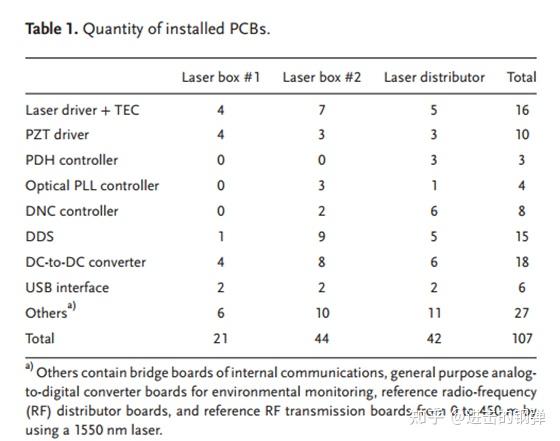
上图为RIKEN搬到东京播送电视塔上的可挪动光钟,此中包罗Laser distributor,2个laser box #1和2个laser box #2,以及2个原子探测室。光谱原子探测室由760*710*550厚的磁屏障质料包裹,而且内部做了4层控温温控在245K,所有所需的激光通过饱偏光纤送入原子实空室,原子实空室实空控造在E-8Pa级别,在实空室下面则包罗了离子泵控造器、BBR shield温控(即冷腔温控),线圈的电流控造器,时序输出板以及PC电脑(运行Labview法式以及通过USB I/F总线形式控造各路PCB板输出)。
在RIKEN的钟光是通过一个斗室间送到原子实空腔,在那个尝试中则是接纳了秒稳1E-15的钟激光,当然后续也可通过锁相环的体例将远端不不变度高的钟光将不不变度传到可搬运光钟上;
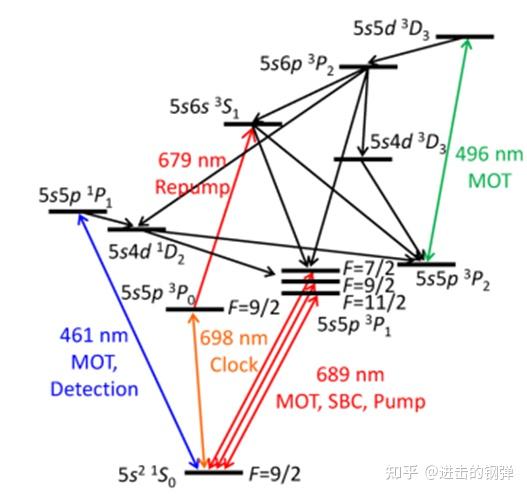
RIKEN 87Sr energy level
Katori组区别于以往的87Sr冷却计划,在一级冷却中参加了496nm那个绿mot和461蓝mot配合构成一级冷却,原因在于经1S0→1P1激发的原子会有相当部门落到3P1和3P2态上,构成“冷却黑洞”,通过参加496nm MOT(3P2 F=13/2 → 3D3 F=15/2)可有效增加冷却效率,而且该能级的饱和光强也较低,仅需3mW,1.5cm曲径即可到达2倍饱和光腔,整个496MOT所利用功率20mW满足需求。最末两级冷却后拆载到14uK阱深的晶格中,各温度和相关阱深如下
87Sr (I=9/2)
1st stage MOT: 1S0 (F=9/2)→1P1 (F=11/2) 461nm, 3P2(F=13/2)→3D3(F=15/2) 497nm; a few mK
2nd stage MOT: 1S0(F=9/2)→3P1(F=9/2,11/2) 689nm; a few μK
Load into a 1D optical lattice at 813nm with a trap depth 14μK
其原子实空探测安装如图

在可搬运光钟中除了前面[11]需要用到的冷腔,还接纳了腔加强手艺:将两束对打晶格均参考在部门反射镜上,使得晶格光在蝴蝶腔内来回振荡在有限功率下加深束腰处的势阱深度。
通过那两项次要手艺将可挪动光钟不确定度拉到了E-18量级
别的利用的自旋极化态造备能级和轴向边带冷却能级和成果如下
Spin polarization:
1S0 (F=9/2, mF=±9/2)→3P1(F=7/2, mF=±7/2)
Axial direction vibration cooling: 1S0→3P1(F=11/2) results: n<0.1
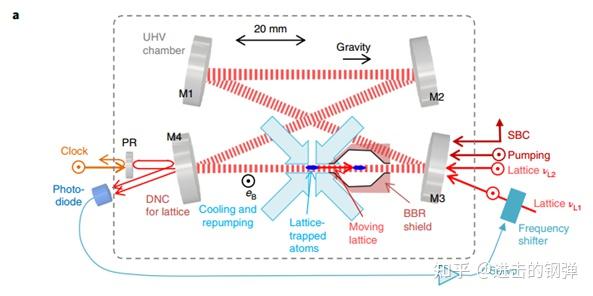
RIKEN可搬运87Sr光钟冷腔与腔加强部门原理图
此中在时序上就间接搬以前总结了:(In BBR shield) Spin polarization → Sideband Cooling → Clock laser interrogation →transport atoms outside of BBR shield → repumping → laser induced fluorescence probing(normalize the excited fraction of atoms)
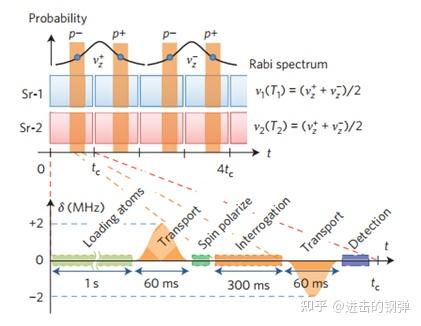
[11]部门时序
前面是RIKEN可搬运87Sr钟的原理介绍,下面是他们详细怎么实现的。
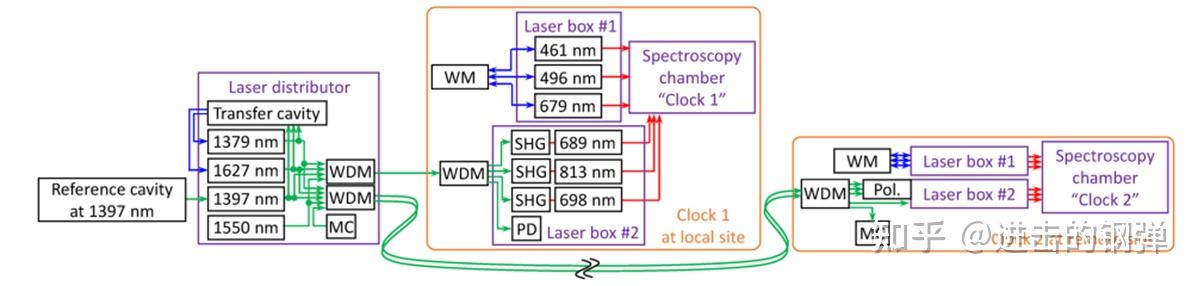
Schematic diagram of a pair of Sr optical lattice clocks. MOT, magneto-optical trap; SBC, sideband cooling; BBR, blackbody radiation; PD, photodetector; SHG, second-harmonic generator; Pol., polarization controller unit; MC, media converter; WM, wavelength meter; WDM, wavelength
整个光钟系统所需要用到的激光可大致由以上框图介绍,别离为参考到超稳腔上的1397nm(698nm钟光的基频光),以及laser distributor(那里面包罗了1379nm,自旋极化以及二级冷却的基频光;1627nm,晶格光的基频光;1550nm,操纵幅度调造用于传输Rb钟的RF信号和trigger信号的激光,别的还有传输腔用于进步1627nm和1379nm光的频次不变度,以及Media converter锁包罗的1490nm和1590nm激光用于PC的通信,四路光均利用波分复用通信波段光纤停止传输而且均配有带宽10kHz的多普勒相位噪声按捺器DNC用于按捺光纤长度对光程影响引起的相位噪声,以包管激光传输的不不变度),laser box #1和laser box #2(ECDL 461nm,496nm,679nm,因为响应能级关于线宽要求较低,均锁定在波长计上,而波长计是操纵钟光校准的;别的则是经波分复用通信光纤传输的1397nm、1627nm、1379nm经倍频得到的自旋极化&二级冷却光、晶格光、钟激光颠末恰当的移频送入实空原子探测室)。
(里面的每一项、每一个小模块,都是极为复杂的尝试,而且仅是大致框图就如斯复杂,能够想象能实正实现是一件多么振奋人心的工程了!)
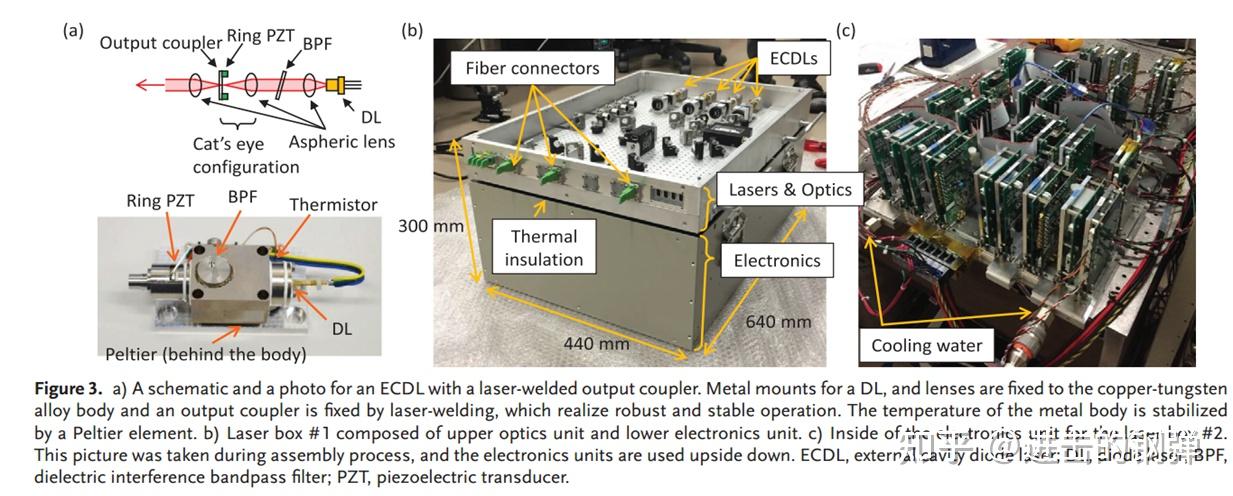
那里就简单看下他们的细节吧,更多细节能够去[12]里认真阅读,他们做了极好的控温(光路的、电路的铝造热沉),ECDL的设想、光路的设想。
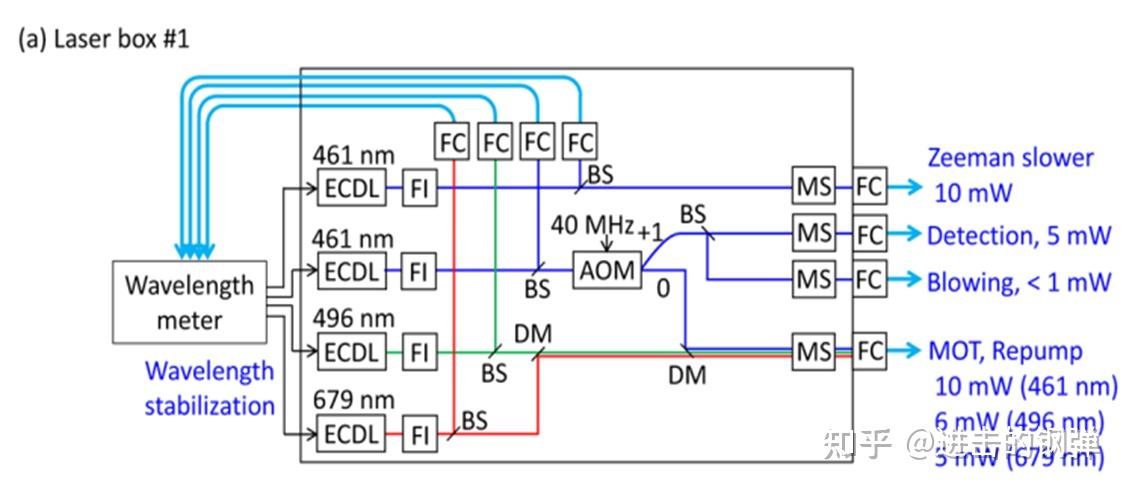
Optical configuration for laser box #1 (461, 496, 679nm) FI, Faraday isolator; FC, fiber coupler; AOM, acousto-optic modulator; MS, mechanical shutter; BS, beam splitter; DM, dichroic mirror; TA, tapered semiconductor optical amplifier; PPLN, periodically- poled lithium niobite;
Optical configuration for laser box #1 (461, 496, 679nm) FI, Faraday isolator; FC, fiber coupler; AOM, acousto-optic modulator; MS, mechanical shutter; BS, beam splitter; DM, dichroic mirror; TA, tapered semiconductor optical amplifier; PPLN, periodically- poled lithium niobite; EOM, electro-optic modulator; VBG, volume Bragg grating; PLL, phase-locked loop; DNC, Doppler noise canceller; DDS, direct digital synthesizer, DPFD, digital phase-frequency discriminator; VCO, voltage-controlled oscillator
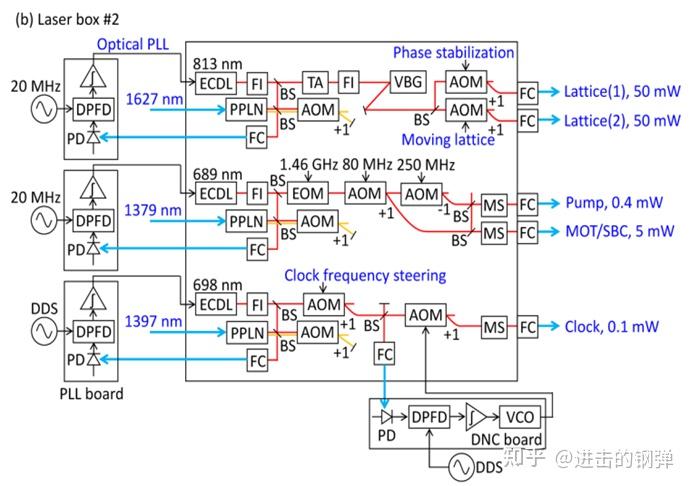
Optical configuration for the laser box #2(689nm, 698nm, 813nm) FI, Faraday isolator; FC, fiber coupler; AOM, acousto-optic modulator; MS, mechanical shutter; BS, beam splitter; DM, dichroic mirror; TA, tapered semiconductor optical amplifier; PPLN, periodically- poled lithium ni

Spectra of a 813 TA output without VBG(red line) and with VBG(blue line). The spectrum was measured using an optical spectrum analyzer with a resolution bandwidth of 1nm and an input power of 1mW. Dashed line shows the wavelength dependence of the diffraction efficiency of the VB
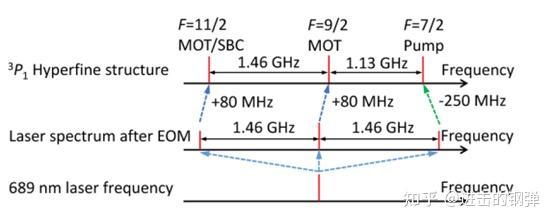
Frequency diagram for a 689nm laser
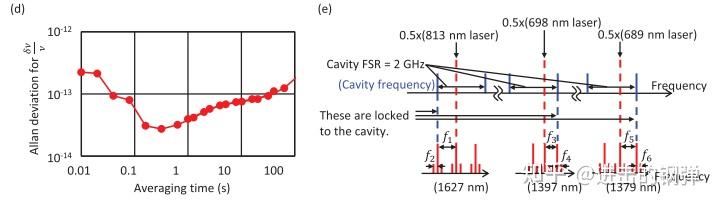
d) The fractional frequency instability of the optical transfer cavity in the laser distributor. e) Frequency diagram in the laser distributor to lock the lasers to the cavity and to tune to target frequencies
里面有十分多的细节,包罗能级失谐量与AOM频次的选择,EO的调造,调造边带的幅度,边带与载波的别离;晶格光VBG光谱的纯化,电路上DDS的分配,trigger信号等;

Photo of the optics unit in the laser distributor
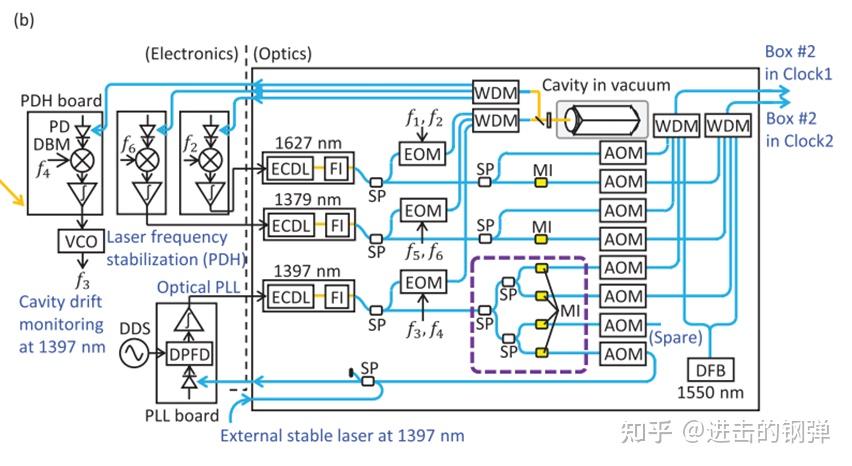
Optical configuration of the laser distributor. Purple dashed region is assembled in an airtight box to reduce changes in temperature and pressure because this part is critical for the residual Doppler noise
别的说下他们的射频信号基准来源,尝试里所有的射频信号均来源于Rb钟所供给的参考,RF reference signal & trigger signal– Rb (Stanford Research System, PRS10, Uncertainty 5E-10) 20MHz 75 MHz, Amplified modulator through 1550nm,两台钟的同步信号则类似于20MHz,为75MHz的幅度调造获得;
关于光纤相位噪声按捺,或者说多普勒噪声按捺,或者...(叫法良多),但总结就是按捺光纤因空气活动、温度起伏等引起的长度变革进而招致的光程变革。
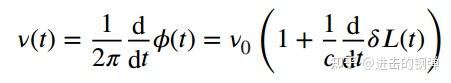
光纤光程变革引起的相位变革(相位噪声)
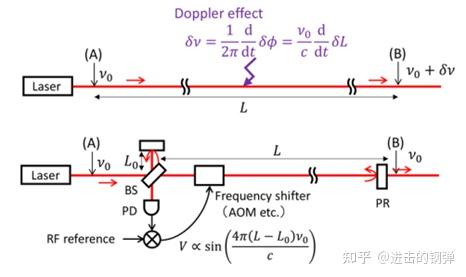
Doppler effect in optical frequency transfer, and phase noise(Doppler noise) cancellation based on Michelson interferometer(AOM: acousto-optic modulator, BS: beam splitter, PD, photo detector, PR: partial reflector)

Configuration of a Doppler noise canceller(DNC) with all-fiber Michelson interferometer (MI)
要到达光钟所能供给的E-16@1s那个程度,他们也做了一些工做[13],总的来说就是要做温控(<1mK)、完全隔断空气活动,才气获得满足现有E-16@1s的光钟那么好的频次信号传递要求.
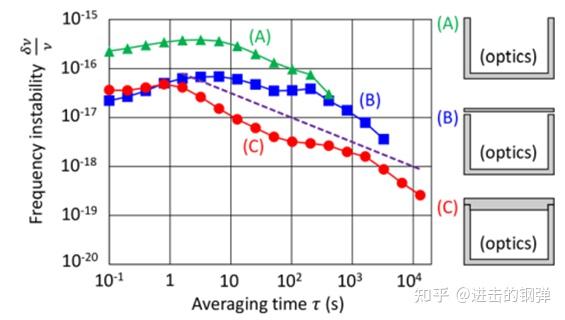
Frequency transfer instability depending on environmental conditions of optical components(dotted line shows instability of optical lattice clock)
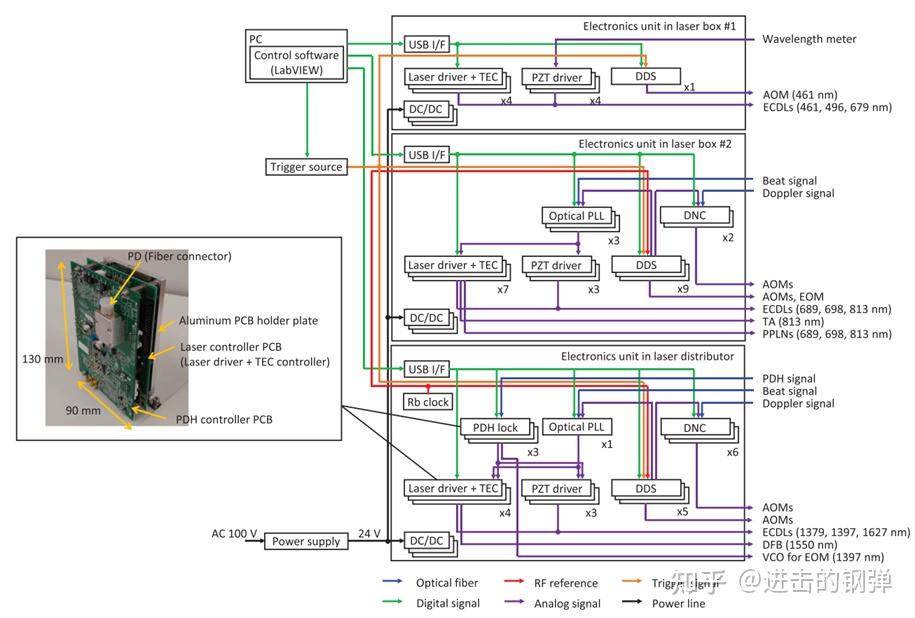
Block diagram of the control system for the laser boxes #1, #2, and the laser distributor. Inset shows a PDH controller combined with a laser controller by using a stacking connector. These PCBs are mounted on aluminum plates that are fixed on the water-cooled plate for the heat
别的Katori组另一个牛逼的处所在于所有的光钟所需的射频电路等包罗激光器的电流驱动、PZT驱动、DDS射频发作器、光学锁相环、多普勒相位噪声按捺器、PDH锁定等都能集成在若干块PCB上,而且最初可以通过USB I/F总线体例用一台电脑最多能够控造512个PCB模块,他们还别离统计了各个激光模块所需要的电路功耗Power supply: Laser box #1 77W;Laser box #2 230W;Laser distributor 192W,
在做出以上成果后,他们还记录了将两台光钟从RIKEN loading到卡车上,在驾驶去往东京塔和unloading过程中的加速度变革和持续时间
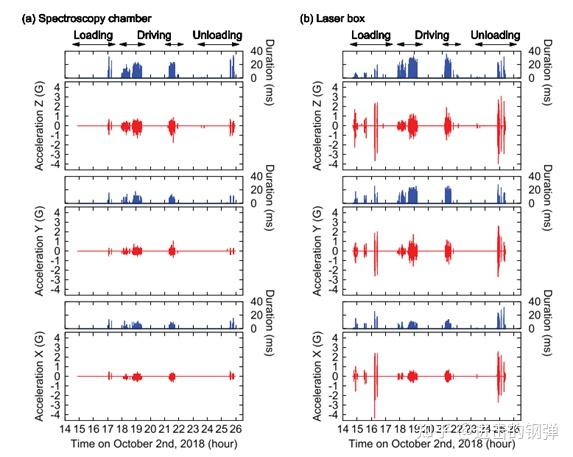
Acceleration monitor for a) the spectroscopy chamber, and b) the laser box #1 during transportation from RIKEN to Tokyo SKYTREE on Oct. 2nd, 2018. Red, and blue lines stand for acceleration peak, and its duration, respectively. Plots for Z-direction (vertical) are shifted by 1 G
那项工做实在让人服气
1.2.3 加州理工可读出单个原子形态的“光镊”光钟/原子阵列光钟[14](atomic- array optical clock,没看到正式的中文翻译,暂那么叫着)那项工做是考虑了离子钟和晶格光钟各自的特征,一个是单离子可长时间囚禁,但因为是单个离子不成制止不不变度秒稳较差;晶格光钟因为是喷一次原子,探测一次,读出的是一系列原子的均匀,因而考虑操纵AOD(能够输入多个频次产生多个衍射光栅叠加的等效AOM)通过恰当的光路设想行程摆列式的光镊,光镊囚禁造备的冷原子到达较长的相关时间

Atomic array optical clock

Fractional Allan deviation obtained via self-comparison to be 2.5×〖10〗^(−15)∕√

Systematic evaluation of clock shifts with tweezer depth and wavelength
接纳那种办法在量子计算平台上拥有读出单个原子形态的才能那个长处,但不成制止在光钟上因为每个光镊之间的相对频差,(他们也做了尝试测得了那个引入额外的光频移而且做了初步的尝试来处理那个问题)
1.2.4 德国PTB可搬运87Sr光钟测地[15]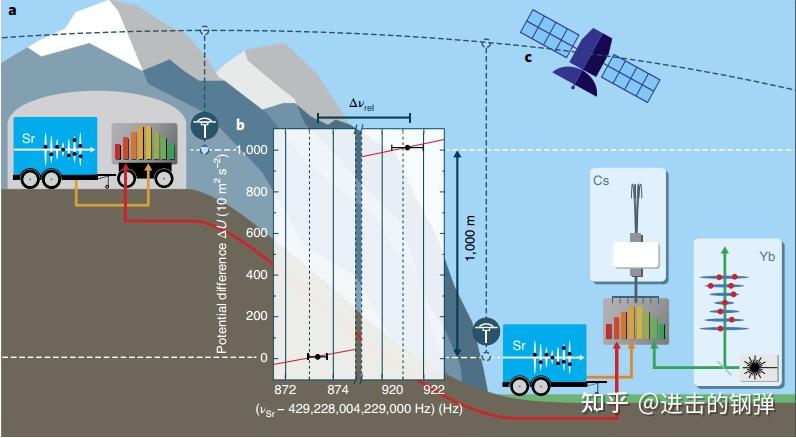
Schematic representation of the measurement campaign. a, For chronometric levelling, the transportable 87Sr optical lattice clock was placed in the LSM underground lab. b, Frequency of the transportable Sr clock as seen by the INRIM Cs fountain clock. The potential difference ΔU
1.2.5 国度授时中心(NTSC)的小型化Sr光钟[16]国度授时中心(中国)也测验考试模块化、小型化Sr光钟而且有了最新的停顿报导
 (b) Layout of the vacuum system(c) Experimental arrangement of all laser beams.
(b) Layout of the vacuum system(c) Experimental arrangement of all laser beams. (b)layout of the 461 nm lase system setup (d) layout of the repumping laser system setup
(b)layout of the 461 nm lase system setup (d) layout of the repumping laser system setup Layout of the second cooling laser system. The insert is the vacuum chamber for the cubic cavity
Layout of the second cooling laser system. The insert is the vacuum chamber for the cubic cavity Differential frequency instability evaluation of the transportable optical clock. The Allan deviation fits to 3.6E-15@1s(red solid line)1.3 199Hg光晶格钟
Differential frequency instability evaluation of the transportable optical clock. The Allan deviation fits to 3.6E-15@1s(red solid line)1.3 199Hg光晶格钟
Hg因为具有比拟Sr和Yb相对较小的BBR系数也被做为光晶格钟的备选原子,次要研造单元有东京大学、LNE-SYRTE、中科院上海光机所、日本理化研究所RIKEN
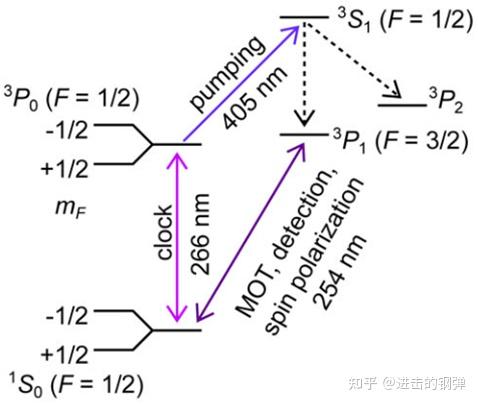
Relevant energy levels for 199Hg with a nuclear spin I=1/2.
比力费事的是Hg所需要的钟跃迁266nm和冷却光&极化光254nm均比力难以获得,RIKEN在2015年报导了Hg的钟跃迁谱[17, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2015, 114(23): 230801.]
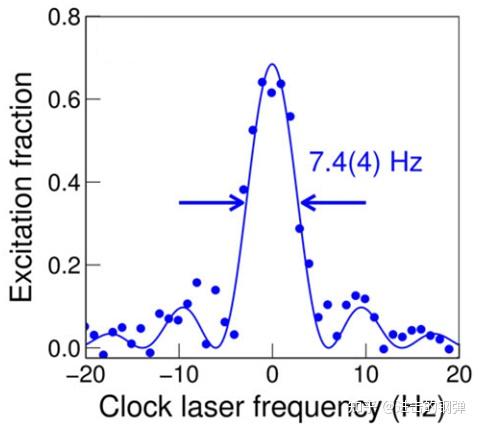
A clock spectrum of the 1S0-3P0 transition of 199Hg.
RIKEN通过87Sr评估了199Hg钟的系统不确定度为7.2E-17,而且丈量了响应的频次比率v_Hg/v_Sr=2.629 314 209 898 909 60(22) ,比值的相对不确定度为8.4E-17
国内次要研造单元为上海光机所,其Hg钟相关尝试安装:

Vacuum chamber

531 nm laser

cooling pump

ULE cavity
 1.4 Mg光晶格钟
1.4 Mg光晶格钟
Mg因为同样对BBR不敏感也是一种备选原子[18]
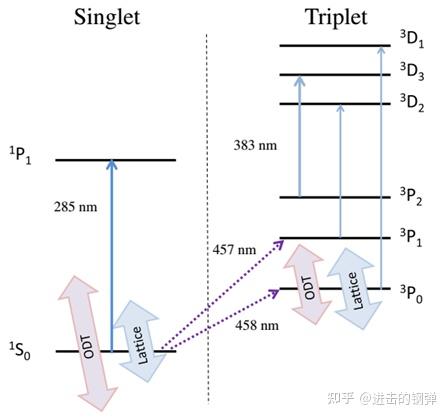
Optical transitions in 24Mg relevant for optical lattice spectroscopy.
因为领会不多我就间接粘PPT上的了
•Atoms are continuously loaded into the long-lived electronic state 3P0 inan optical dipole trap (ODT) at 1064 nm using a dual MOT.
•Atoms trapped in a MOT using the 1S0-1P1 transition are optically transferred with 457 nm light to the 3P1 state and then to 3P2.
•The atoms are further cooled in a MOT with 383 nm light that excites the 3D manifold, and cold atoms are permitted to accumulate in 3P0 in the ODT.
•The 458 nm light interrogates the magnetic –field-enhanced clock transition
俄罗斯在2017年[21]报导了Mg钟的频标程度
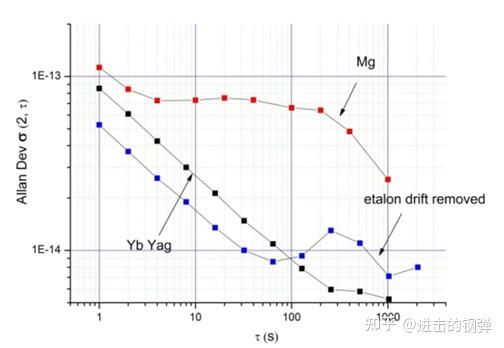
Allan deviation for the Mg frequency standard
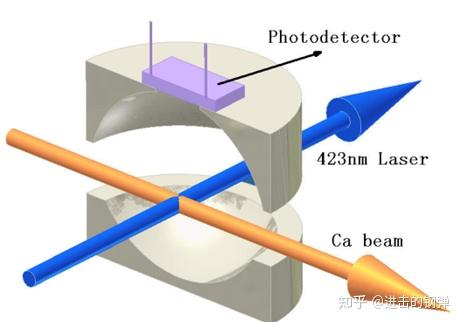
1.5 Ca光钟准确说Ca光钟更多的是热原子束流的光钟,而且Ca目前做的好的是武汉物数所的Ca+钟;
在热原子束流Ca钟方面北京大学陈景标教师组做了一些工做[22],报导了不不变度秒稳3E-14,长稳1.8E-15@1600s

Atomic energy levels related to calcium beam optical clock, where line 423 nm is for detection while line 657 nm is for clock transition .
The effective collection of the fluorescence can improve the signal intensity .Using this device, the fluorescence collection efficiency up to 80% can be achieved

A fully vacuum-sealed calcium beam tube

Calcium beam tube with a flange structure
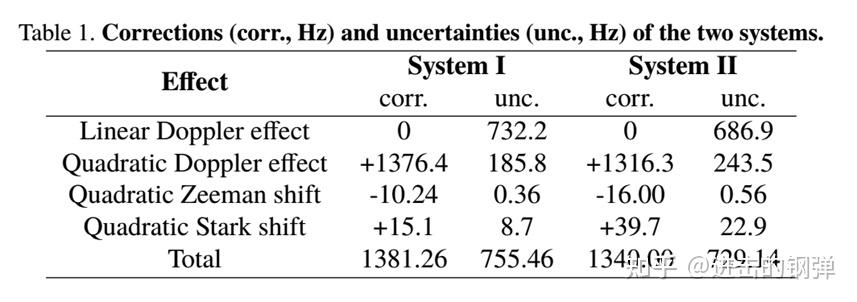 二、离子光钟
二、离子光钟
A few of years ago, H.Dehmelt(Nobel,1989) proposed:
“A individual atomic ion localized in the center of a small Paul RF quadrupole trap has potential as an ultimate laser frequency standard……”
离子光钟有以下几个长处:
Ion optical clock has a lager transition frequency at 1015 order.
Ion can be brought to a “state of complete rest in free space” by laser cooling, all Doppler effects vanish.
“Electric trapping field vanishes at centre of trap and there is on (effective) Stark effect”
Collision free regime at UHV conditions for single ion
“Million-fold amplification of single ion fluorescence” by Quantum Jump detection of a dipole forbidden transition via a coupled strong transition.
典型的离子光钟有以下几种形式[2]:
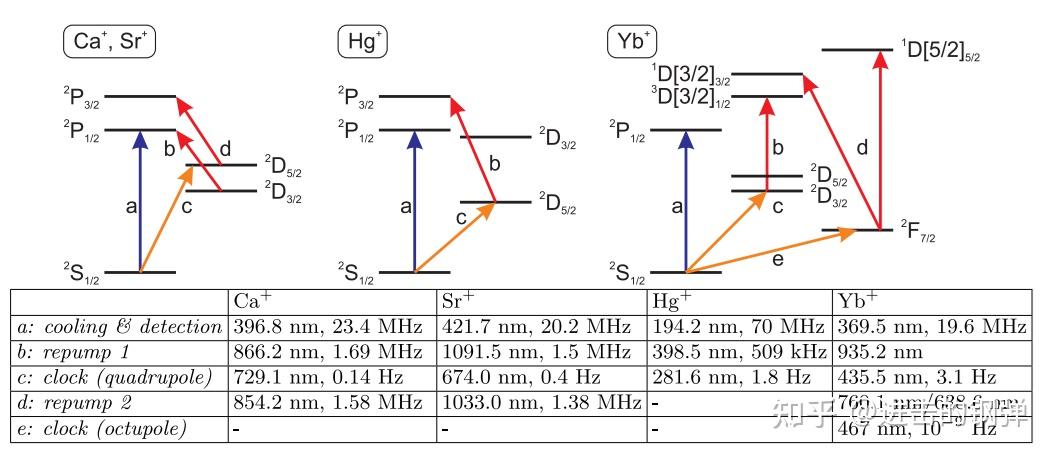
Schematic energy level diagram of clock ions with a single valence electron and Yb+, together with a table of the most relevant transition wavelengths and linewidths. Energy levels are not to scale and the term notation follows Martin, Zalubas, and Hagan (1978).
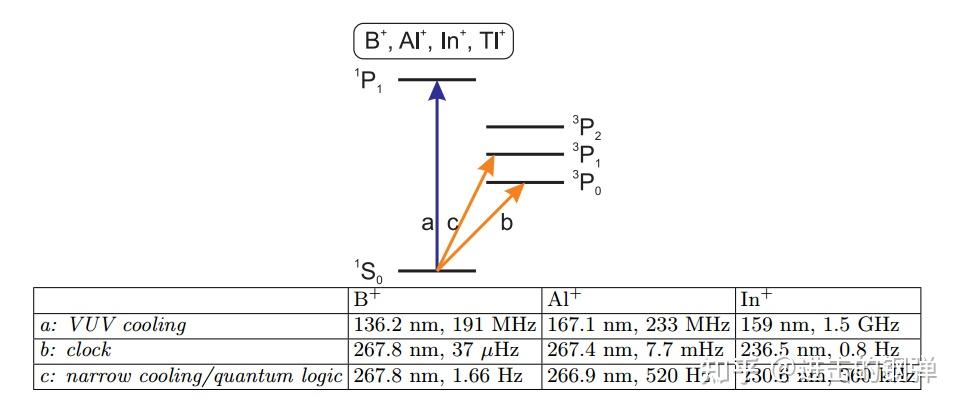
Schematic level structure of ion clocks based on group 13 (formerly group IIIA) singly charged ions, together with a table of the most relevant transition wavelength and linewidths. Data are from the NIST database(Ralchenko et al., 2012). Energy levels are not to scale.
典型的离子光钟工做原理:5
(1) 通过电离手段获得离子 (2)操纵paul阱囚禁和拆载离子(88Sr+,87Sr+, 199Hg+, 171Yb+, 40Ca+, 43Ca+, 27Al+,138Ba+, 115In+…)
钟探询时序:
(3) 多普勒冷却、边带冷却、协同冷却 (4) 态造备与钟探询 (5) 离子频标的闭环 (6) 不不变度和不确定度的评估
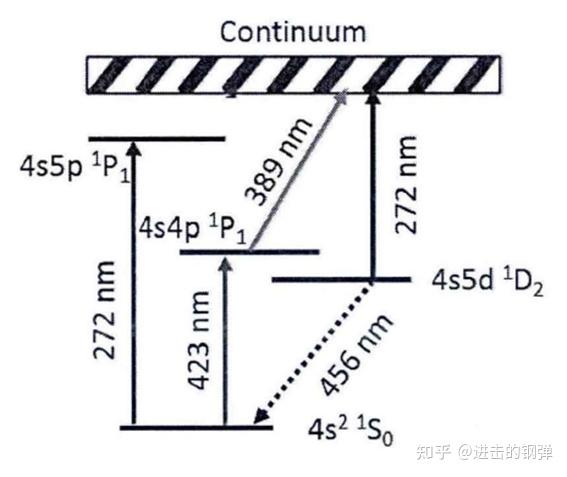
Simplified Energy level schemes of 40Ca
Ca 的电离过程,40Ca → 40Ca+ :
1)4s^2 〖(_^1)S〗_0-4s4p〖(_^1)P〗_1 423nm
2)4s5p〖(_^1)P〗_1 -continuum energy level >389nm
操纵时变电场囚禁单离子:
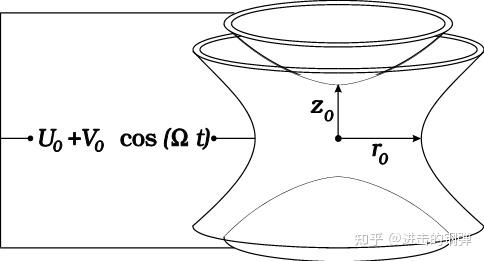
Axial (z) and Radial( r) confinement is provided by a rapidly oscillating quadratic potential created by the electrode configuration. Solution of the equation of motion shows that the ion moves within a time-averaged 3-D potential well.


多普勒冷却和边带冷却(在光晶格钟也常用)
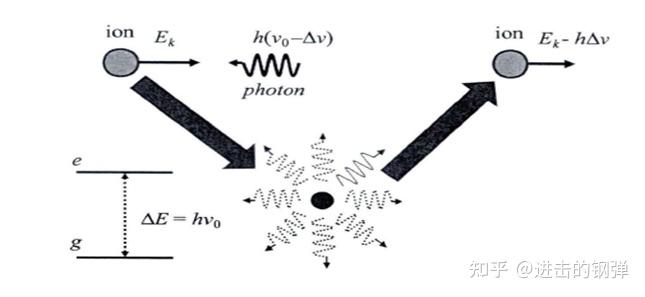
Simplified schematic diagram of Doppler laser cooling . The ion absorbs a photon with energy ∆ =ℎ _0, and emit a photon with energy ℎ( _0−∆ ). Thus, the ion will experiments a net energy change ℎ∆
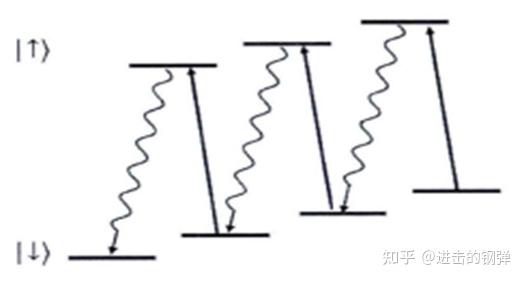
Illustration of sideband cooling. Ion acts as a quantum harmonic oscillator. The ion jumps into a excited state by absorb a photon, and then back to ground state by spontaneous emission. In the process, the vibration quantum number has reduced 1,amount to the ion loss energy ℎΔν
协同冷却:
Sympathetic cooling is a process in which particles of one type cool particles of another type.
Typically, atomic ions that can be directly laser cooled are used to cool nearby ions or atoms, by way of their mutual Coulomb interaction. This technique allows cooling of ions and atoms that cant be cooled directly by laser cooling.

(1) Cooling with different isotopes[] (2) Cooling with different ion species
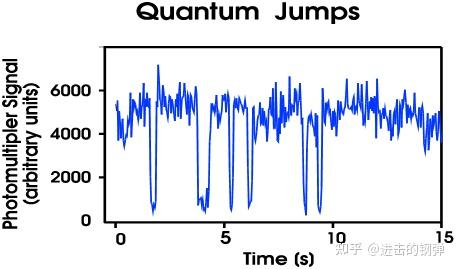
确定获得单离子的手段:Quantum Jumps
Ion cycles between states 1 and 2 high fluorescence rate
Occasionally ion makes ‘quantum jump’ into state 3 (metastable state). Fluorescence switches off.
The absence of a large number of 1-2 photons accompanies the absorption of a single 1-3 photon.
Use to detect weak (narrow) trans. - Clock

Through the observation of quantum Jumps in the fluorescence , we can detect the absorption of single photons by a single ion.
某些离子因为能级所需激光器无法实现无法构造出闭合的跃迁体例,需要通过量子逻辑光谱的体例操纵逻辑粒子辅助判断钟光能否与光谱粒子共振
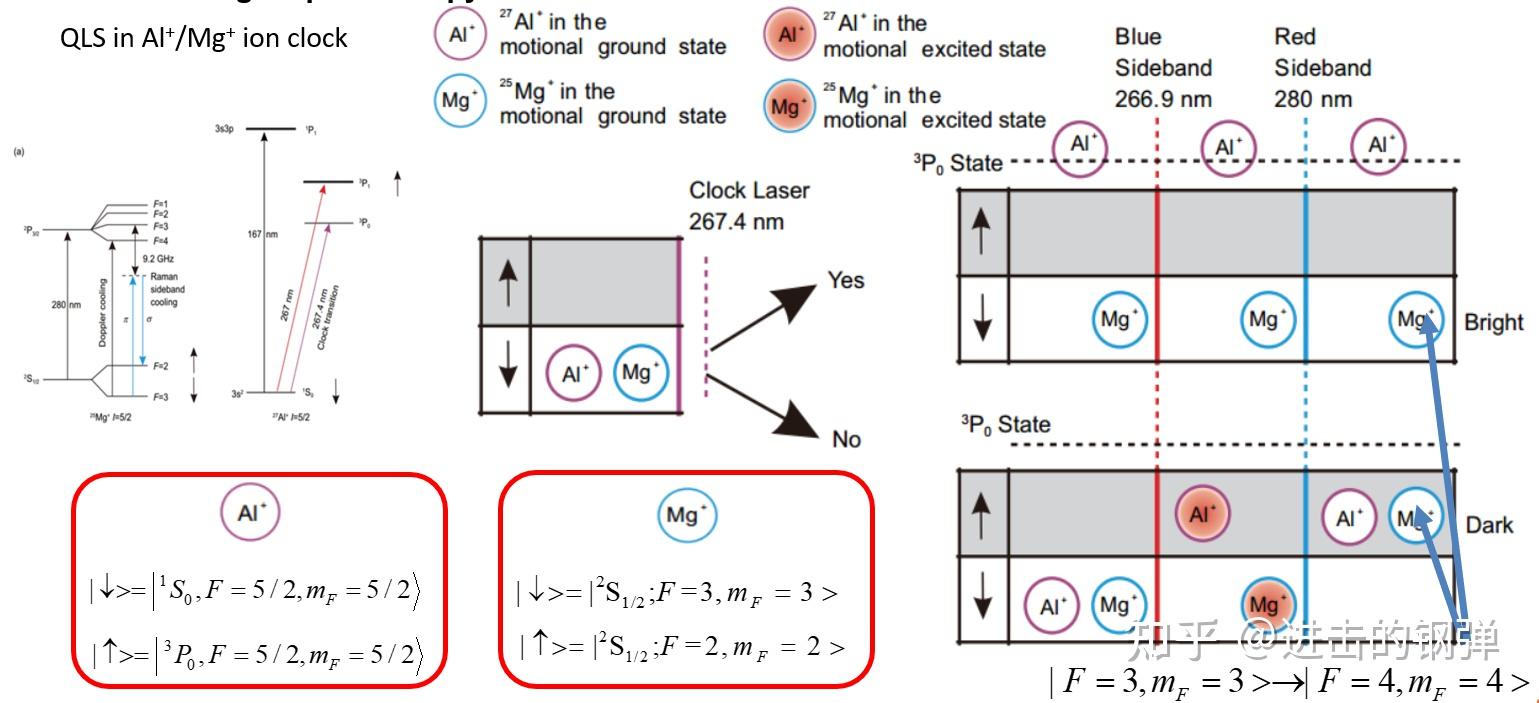
Quantum Logic Spectroscopy Procedure
离子光钟的闭环计划Closed-loop locking
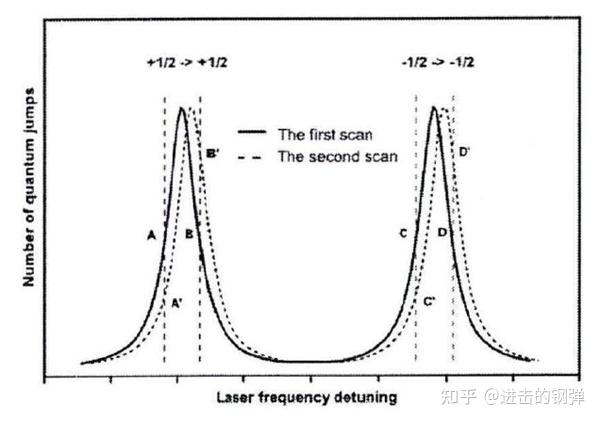
Illustration of four point locking scheme. To reference the clock laser to the clock transition, the laser is locked to the resonance center using a feedback loop. The number of quantum jumps is measured on one side of resonance, then the clock laser is stepped by the full width
在离子光钟的研造方面次要有以下科研单元停止了相关离子的尝试
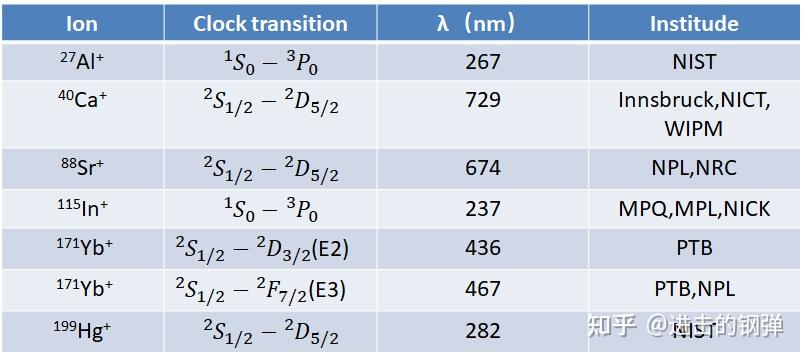
NIST: National Institute of Standards and Technology
WIPM: Wuhan Institute of Physics and Mathematics of Chinese Academy of Sciences
NICT: National Institute of information and Communication Technology
NPL: National Physical Laboratory (The UK)
PTB: Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt
NRC: National Research Council of Canada
MPQ: max-planck-institutfürquantenoptik
MPL: Institute of Optics, Information and Photonics
2.1 Al+离子光钟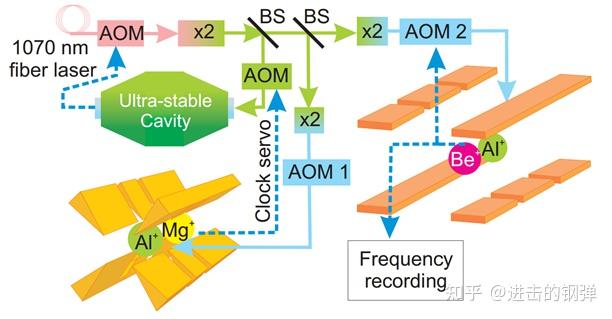
Two Al+ optical ion clocks [23]
两台铝离子光钟,此中一台为Al+/Mg+离子光钟,另一台为Al+/Be+离子光钟,此中Al+是用于闭环的光谱离子,Mg+和Be+均是用于协同冷却和量子逻辑光谱的逻辑粒子(Al+粒子光钟需要用到协同冷却是因为针对Al+ 1S0→1P1的166nm持续极紫外光太难获得了,但印象中仿佛国内有个科研小组和国内做Al+钟的合做搞出来了,详细文章忘记了)
NIST报导的Al+钟的不不变度和不确定度,(后来他们还拿Al+钟和JILA结合Yb、Sr、Al做到了不确定度到E-18的频次比率丈量尝试,阿谁BACON也是个大工程,有空再更)
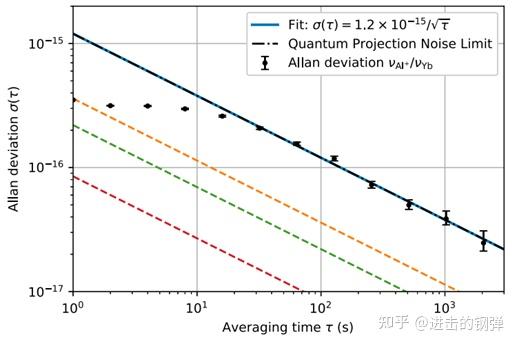
Allan deviation of the frequency ratio _( ^+ )∕ _ measured over ~23000 s. The asymptote is fit to extract a frequency stability of ( )=1.2×〖10〗^(−15)∕√
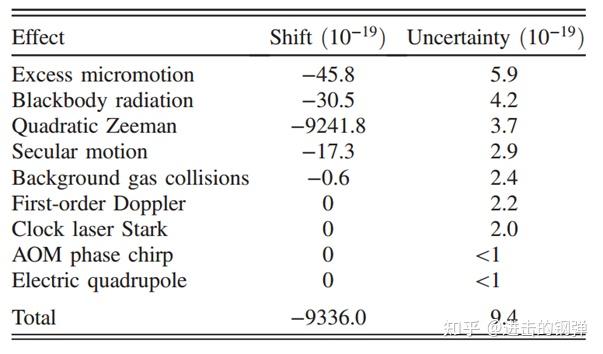
Fractional frequency shifts (Δ ∕ ) and associated systematic uncertainties for the 27Al+ quantum-logic clock
2.2 Sr+离子光钟(2020/08/17 9:35 开更)
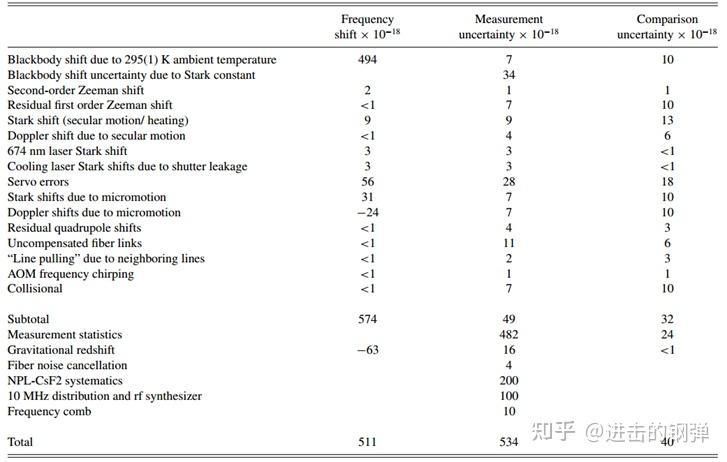
Uncertainty budget for the 2012 two-trap comparisons and absolute frequency measurements.(NPL)
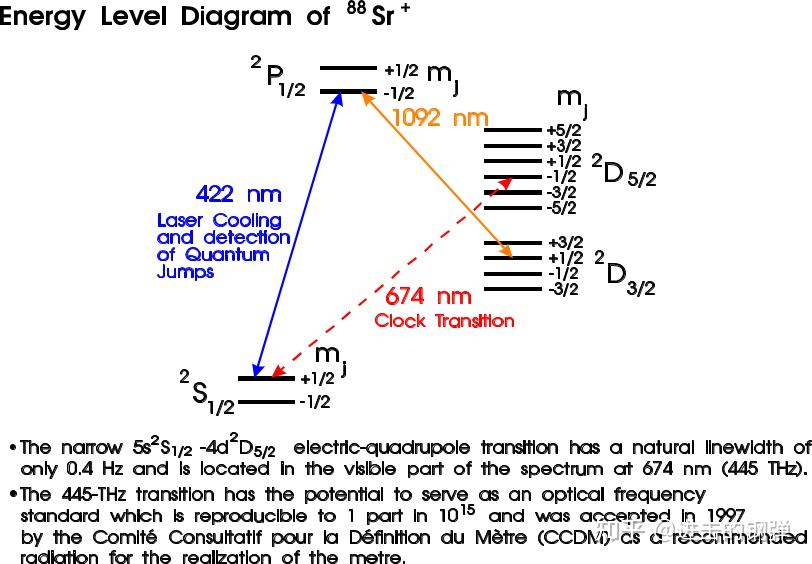
2.3 Yb+离子光钟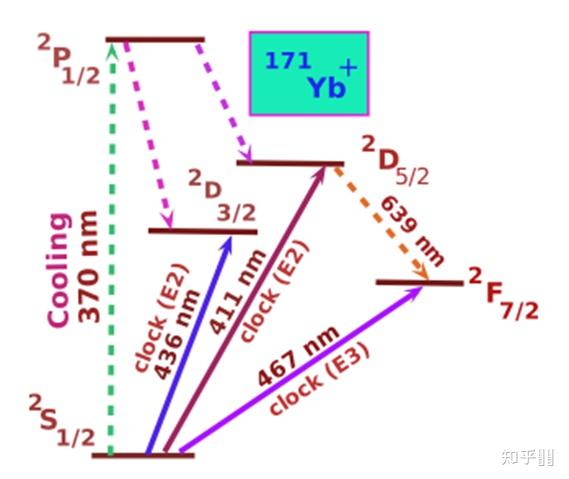 Schematic view of the energy levels and the clock transitions in the 171Yb+ ion.
Schematic view of the energy levels and the clock transitions in the 171Yb+ ion.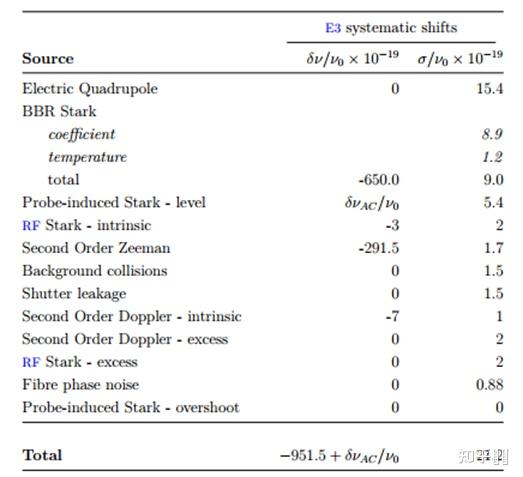 Total systematic uncertainty budget of the 171Yb+ clock operating on the E3 transition.(C. Baynham PhD, Oxford[24]) 2.4 Ca+离子光钟
Total systematic uncertainty budget of the 171Yb+ clock operating on the E3 transition.(C. Baynham PhD, Oxford[24]) 2.4 Ca+离子光钟
Ca+离子光钟当属物数所开展较早,近期也有目标更新,是在长稳能逃上光晶格钟不不变度的为数不多的离子光钟,那方面物数所高克林教师,管桦教师的良多博士和硕士论文中有良多细节。
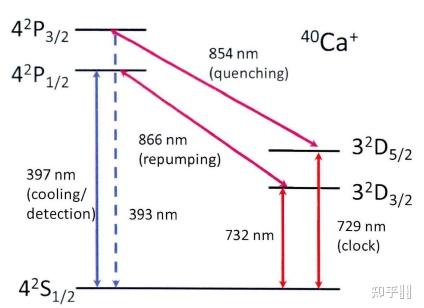 Simplified level schemes of 40Ca+ ions.
Simplified level schemes of 40Ca+ ions.Laser light exciting the 〖(_ ^2)S〗_(1/2)-〖(_ ^2)P〗_(1/2)transition is called “cooling/detection laser light”;
laser light exciting the (n - 1)d 〖(_ ^2)D〗_(3/2) -np 〖(_ ^2)P〗_(1/2)- transition is called “repump laser light”.
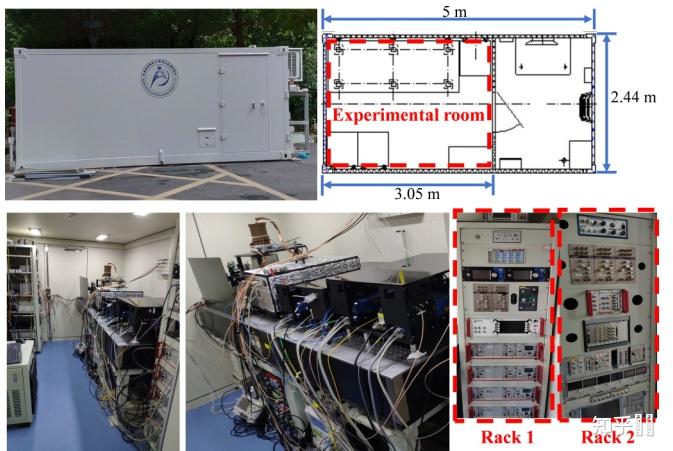 WIPM&amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;#39;s transportable Ca+ ion optical clock
WIPM&amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;#39;s transportable Ca+ ion optical clock2020年物数所报导了搬到北京计量院比对的可搬运钙离子光钟[25],此中次要为不确定度和不不变度的进步成果。
不确定度从17年[24]的7.3E-17进步到2020年的1.3E-17,次要由BBR限造;温度不确定度小于8K时,BBR不确定度<1E-16
次要加拆热屏障层、空调控温使得温度颠簸小于1K,被动隔振、设想对振动不敏感的参考腔,抗磁光学平台,多层磁屏障手段;半主动化控造系统,实现智能化的光钟锁定;
尝试有里间和外间别离独立控温,尝试房间的温度起伏限造在±2K以内,对腔体的控温使得温度不确定度约1.5K,最末测得相对不确定度为1.3E-17
最末的钟光系统是放置在尝试室情况中(因为拖车上的振动要比尝试室中差1个量级)
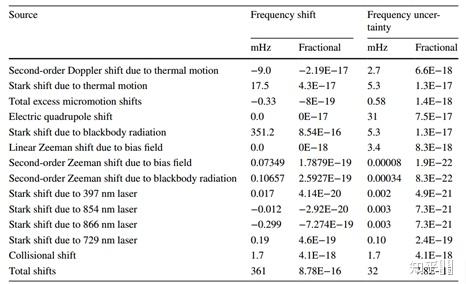 Systematic shifts and uncertainties of the transportable clock @2017[26]
Systematic shifts and uncertainties of the transportable clock @2017[26]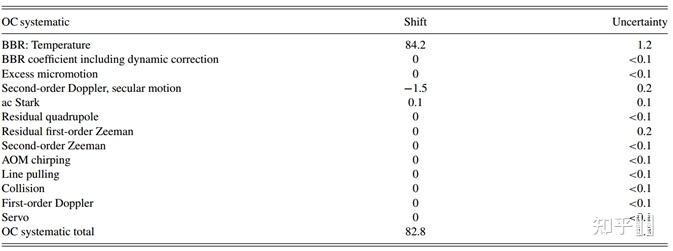 Uncertainty budge for the systematic shifts evaluation of the transportable Ca+ optical clock. Numbers are shown in E-17[25]
Uncertainty budge for the systematic shifts evaluation of the transportable Ca+ optical clock. Numbers are shown in E-17[25]以及最新的不不变度和不确定度[27]
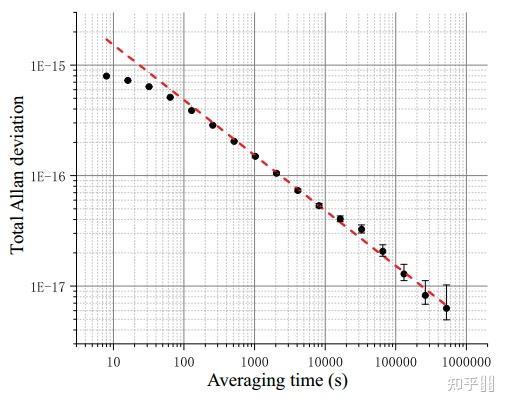 The total Allan deviation measured for a single clock. The stability for a single clock is measured as 4.9(1)E-15@1s and reaches 6.3(+3.9 -1.4)E-18 in an averaging time of 524 000s
The total Allan deviation measured for a single clock. The stability for a single clock is measured as 4.9(1)E-15@1s and reaches 6.3(+3.9 -1.4)E-18 in an averaging time of 524 000s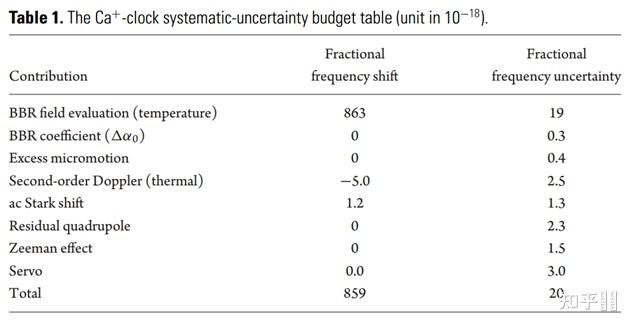 2.5 Hg+离子光钟
2.5 Hg+离子光钟
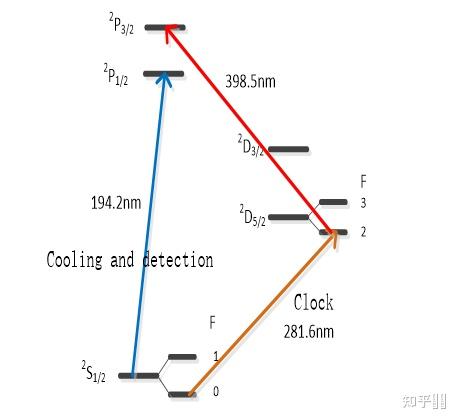 Energy level diagram of 199Hg+
Energy level diagram of 199Hg+ Electrode structure for the spherical Paul trap used in the Hg+ optical clock
Electrode structure for the spherical Paul trap used in the Hg+ optical clock〖(_ ^2)S〗_(1/2)-〖(_ ^2)D〗_(5/2) 1 064 721 609 899 144.94(97)Hz (NIST)
2008年Hg+钟评估成果[28]
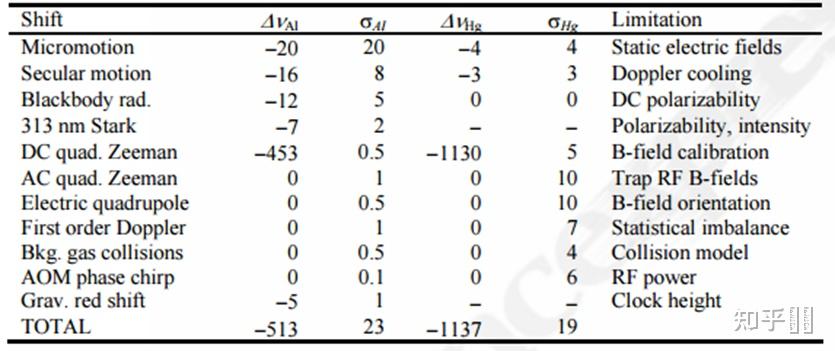 27Al+ 〖(_ ^1) 〗_0−〖(_ ^3) 〗_0 and 199Hg+ 〖(_ ^2) 〗_(1/2)−〖(_ ^2) 〗_(5/2) clock shifts (Δν), and uncertainties (σ) in units of 10−18 of fractional frequency. 2.6 In+离子光钟
27Al+ 〖(_ ^1) 〗_0−〖(_ ^3) 〗_0 and 199Hg+ 〖(_ ^2) 〗_(1/2)−〖(_ ^2) 〗_(5/2) clock shifts (Δν), and uncertainties (σ) in units of 10−18 of fractional frequency. 2.6 In+离子光钟
 Relevant energy levels and transitions in of 115In+
Relevant energy levels and transitions in of 115In+ Schematic drawing of the ion chain configurations for a new approach
Schematic drawing of the ion chain configurations for a new approach  Schematic of the experimental setup. DM: dichroic mirror, PMT: photomultiplier tube, ICCD: image-intensified CCD camera.
Schematic of the experimental setup. DM: dichroic mirror, PMT: photomultiplier tube, ICCD: image-intensified CCD camera. NICT报导了In+绝对频次丈量成果〖(_ ^1)S〗_0-〖(_ ^3)P〗_0 1 267 402 452 901 049.9(6.9)Hz (NICT) [29]
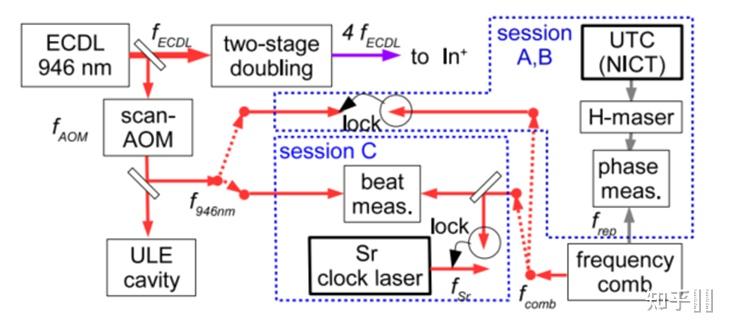 Schematic of the clcok-laser frequency measurement. ECDL: External-Cavity Diode Laser, ULE: Ultra Low Expansion, UTC(NICT): realization of Universal Coordinated Time at NICT.
Schematic of the clcok-laser frequency measurement. ECDL: External-Cavity Diode Laser, ULE: Ultra Low Expansion, UTC(NICT): realization of Universal Coordinated Time at NICT.  Plot of the last six digits of the measured frequency ν0 in three sessions and of their weighed averaged value denoted as the gray line. The two gray dotted lines represent a range of the standard error.
Plot of the last six digits of the measured frequency ν0 in three sessions and of their weighed averaged value denoted as the gray line. The two gray dotted lines represent a range of the standard error. NICT In+离子光钟不不变度和不确定度评估[28]
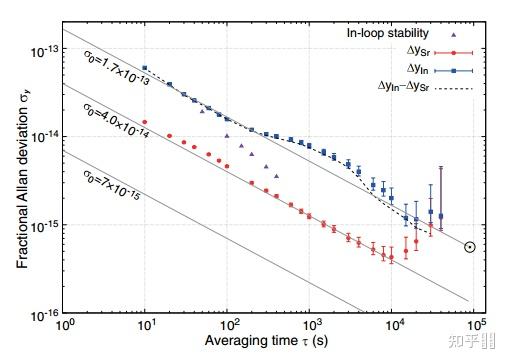 Fractional Allan deviations of ΔγIn(blue squares), starting at 2E-14@50s steering interval
Fractional Allan deviations of ΔγIn(blue squares), starting at 2E-14@50s steering interval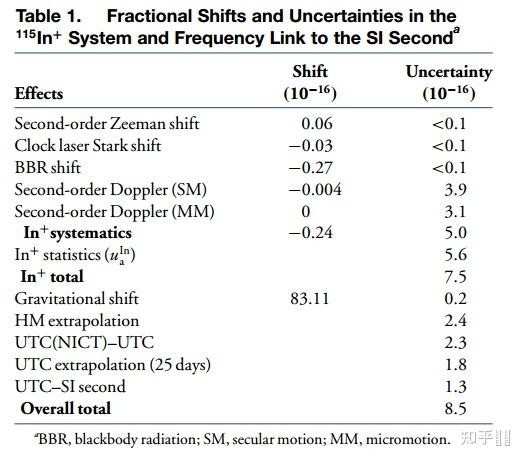 2.7 其他高价离子光钟(Highly Charged Ions, HCIs)
2.7 其他高价离子光钟(Highly Charged Ions, HCIs)
 Schematic diagrams of the low-lying atomic and hyperfine energy levels of the (a) 58Ni12+, (b) 63Cu13+, (c) 106Pd12+, and (d) 107Ag13+ HCIs. Intercombination lines that are apt for the clock and cooling transitions are shown in red and blue, respectively. The estimated wavelength
Schematic diagrams of the low-lying atomic and hyperfine energy levels of the (a) 58Ni12+, (b) 63Cu13+, (c) 106Pd12+, and (d) 107Ag13+ HCIs. Intercombination lines that are apt for the clock and cooling transitions are shown in red and blue, respectively. The estimated wavelengthIt is generally intended to use narrow linewidths (forbidden transitions) in atomic clocks as clock transitions. As the highly charged ions (HCIs) are less sensitive to external perturbations owing to their strongly contracted atomic orbitals , choosing the forbidden transitions from the HCIs is more advantageous for atomic clocks compared with those of neural atoms and singly charged ions, making very accurate optical clocks with the fractional uncertainties below 10-19 level. These HCIs have simple atomic energy levels, clocktransitions with quality factors larger than 1015, and optical magnetic-dipole (M1) transitions that can be used for laser cooling and detecting quantum jumps on the clock transitions by the shelving method.
2.8 核光钟(Th+...等)即剥离所有电子仅剩原子核的核光钟,那类次要黑体辐射BBR更低,而且要求光频更高(向X射线频段标的目的),理论上性能更优,比来很火但开展难度较大
以上离子光钟良多部门都只是摘了部门常用的尝试手段,因为没有参与详细的尝试所以没有写很详细,若是有想深切领会的能够留言一路讨论
3. 其他光钟相关尝试 3.1 光频下转换(Coherent optical clock down-conversion for microwave frequencies with 1E-18 instability)若是说光钟是将钟激光闭环到冷原子上,那么将光频通过光梳转换成射频才算实正意义上将光钟落地(没准将来也会有设备能够间接用钟激光当频次参考呢!?)
那篇[30]2020报导 了将光频下转换到射频繁具有光频的E-18不不变度。
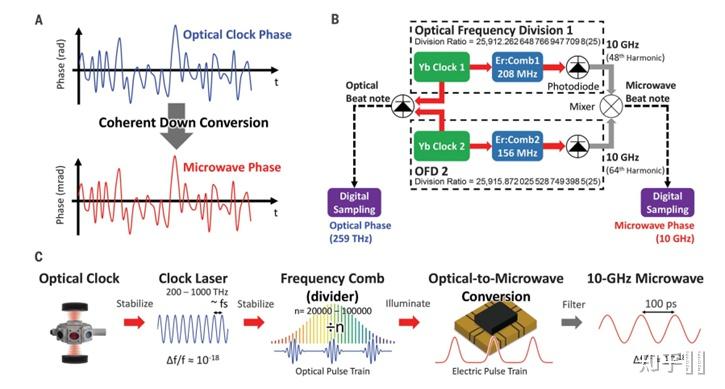 Coherent optical clock down-conversion
Coherent optical clock down-conversion Fractional frequency stability comparison of state-of-the-art sources.3.2 不确定度到E-18级此外光钟时频收集比对(Frequency ratio measurements at 18-digit accuracy using an optical clock network)
Fractional frequency stability comparison of state-of-the-art sources.3.2 不确定度到E-18级此外光钟时频收集比对(Frequency ratio measurements at 18-digit accuracy using an optical clock network)
若是说本科我见过更大规模的合做是ROBOCON角逐(需要机械、电子、光学破费一年时间设想编程造做和联调)
那么到如今搬砖我见过更大规模的合做就是BACON(Boulder Atomic Clock Optical Network (BACON) Collaboration)的那项工做了[31]
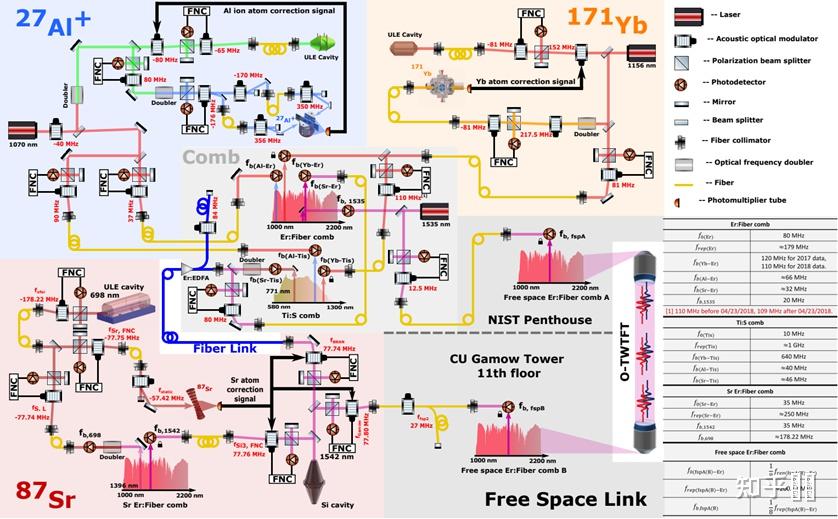 BACON光钟时频收集
BACON光钟时频收集此中包罗87Sr, 171Yb, 27Al+,以及两台光梳停止比对,图中还仅仅包罗钟光的部门,冷原子的部门以及电路的更多细节能够到Arxiv上[32]看,印象中有60+页,仍有良多细节没有表述完全。
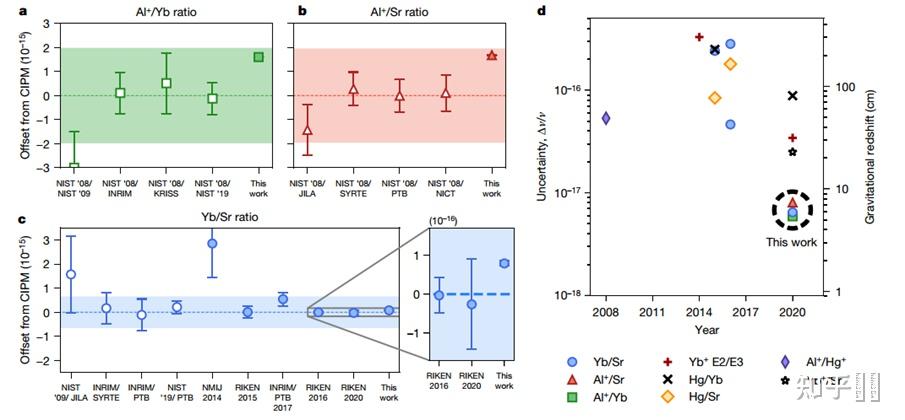 Comparison of measured frequency ratios with previous results.
Comparison of measured frequency ratios with previous results.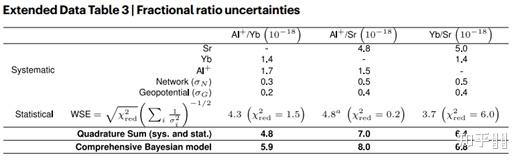
别的他们还用传统评估办法和用统计(贝叶斯后验定理)停止比力,表白有希望在短时间内通过贝叶斯统计的体例快速评估光钟的不确定度
3.3 紧凑型光钟以典型双光子跃迁Rb光钟为例,在进步现有不不变度和不确定度根底上仍连结必然的紧凑可便携特征的光钟(相关于现有芯片式微波Rb而言),典型的有DARPA撑持的NIST研造的微腔光梳[33]和微型Rb光钟[34]
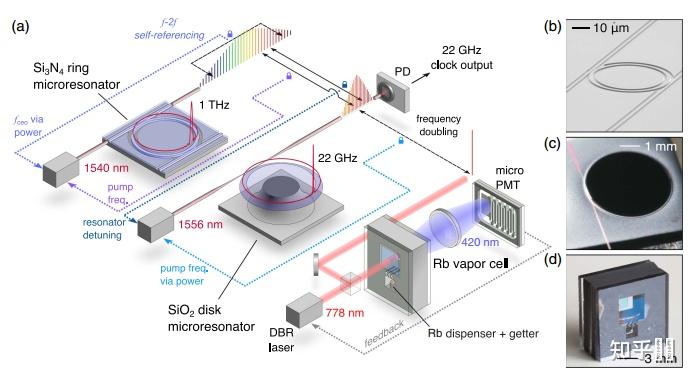 Schematic of the microfabricated photonic optical atomic clock
Schematic of the microfabricated photonic optical atomic clock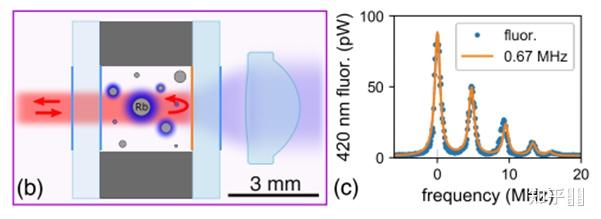 (b) The microfabricated vapor cell has optically coated windows and an aspheric collection optic directs the blue fluorescence from the atoms onto the PMT. (c) Spectrum of two of the hyperfine components of the two-photon transition and corresponding fit showing a linewidth of ~6
(b) The microfabricated vapor cell has optically coated windows and an aspheric collection optic directs the blue fluorescence from the atoms onto the PMT. (c) Spectrum of two of the hyperfine components of the two-photon transition and corresponding fit showing a linewidth of ~6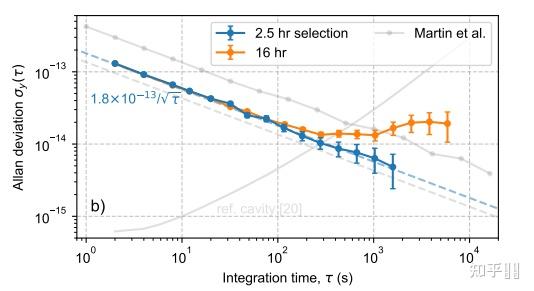 Allan deviations of the rubidium-stabilized clock laser frequency with 1σ error bars
Allan deviations of the rubidium-stabilized clock laser frequency with 1σ error bars(暂时停更,以后有感兴趣的停顿再弥补, to be continued...)
结语
以上仅是对目前光钟的开展停止了相当粗略浅近的介绍,任何一本国表里的博士论文的前沿介绍城市比那个答复详细的多。
别的那些内容仅是对我目前所学的一点记录,以及留下的对后来人的“一点面包屑”,吾辈当自强,勤奋开展祖国的时频程度[35]!
参考文献[1] Chinese Physics Letters, 2014, 31(9): 093201.
[2] Reviews of Modern Physics, 2015, 87(2): 637.
[3] Physical review letters, 1987, 59(23): 2631.
[4] science, 2008, 320(5884): 1734-1738.
[5] NATURE, 87, 564(2018)
[6] Nature, 2018, 564(7734)
[7] Chinese Physics B, 2020, 29(9): 090601.
[8] Metrologia, 2020, 57(6): 065017.
[9] Science, 2017, 358(6359): 90-94.
[10] Nature Photonics, 2015, 9(3): 185-189.
[11] Nature Photonics, 2020, 14(7): 411-415.
[12] Advanced Quantum Technologies, 2021: 2100015.
[13] Electronics and Communications in Japan, 2019, 102(5): 43-48.
[14] Phys. Rev. X 9, 041052 (2019)
[15] Nature Physics, 2018, 14(5): 437-441.
[16] Chinese Physics B, 2020, 29(7): 070602.
[17] Phys. Rev. Lett., 2015, 114(23): 230801.
[18] Phys. Rev. Lett., 2015, 115(24): 240801.
[19] Journal of Physics 793, 012008 (2017)
[20] 2016 IEEE International Frequency Control Symposium (IFCS). IEEE, 2016: 1-4.
[21] Phys. Rev. A 65,040304(2002)
[22] Phys. Rev. A 68,042302(2003)
[23] Phys. Rev. Let., 2019, 123(3): 033201.
[24] Baynham, C. (2018). Frequency metrology at the 10^−18 level with an ytterbium ion optical clock [PhD thesis]. University of Oxford.
[25] Applied Physics B, 2017, 123(4): 1-9.
[26] Physical Review A, 2020, 102(5): 050802.
[27] Natl. Sci. Rev., 2020, Vol. 7, No. 12
[28] Science, 2008, 319(5871): 1808-1812.
[29] Opt. Expr., 2017, 25(10): 11725-11735.
[30] Science, 2020, 368(6493): 889-892.
[31] Nature, 2021, 591(7851): 564-569.
[32] arXiv preprint arXiv:2005.14694, 2020.
[33] Optica, 2019, 6(5): 680-685.
[34] arXiv preprint arXiv:2105.00610, 2021.
[35] 王义遒. 我国早期原子钟研造过程回忆[J]. 宇航计测手艺, 2020, 40(1): 1.
